
Pearn WL, Wu CW (2006a) Critical acceptance values and sample sizes of a variables sampling plan for very low fraction of defectives. Pearn WL, Shu MH, Hsu BM (2005) Monitoring manufacturing quality for multiple Li-BPIC processes based on capability index C pmk.
#Sequential testing Pc
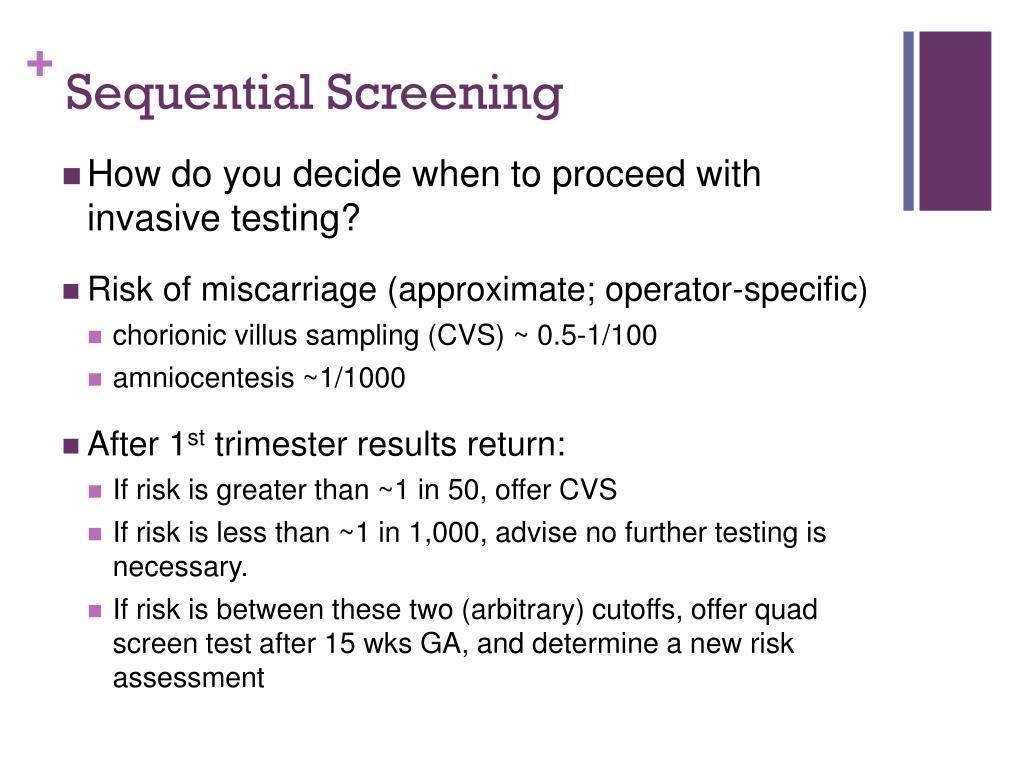
Pearn WL, Lin PC (2004) Testing process performance based on capability index C pk with critical values. Pearn WL, Lin PC (2002) Computer program for calculating the p-value in testing process capability index C pmk. Pearn WL, Kotz S (2006) Encyclopedia and handbook of process capability indices: a comprehensive exposition of quality control measures. Pearn WL, Chen KS (1999) Making decision in assessing process capability index Cpk. Negrin I, Parmet Y, Schechtman E (2011) Developing a sampling plan based on C pk-unknown variance. Negrin I, Parmet Y, Schechtman E (2009) Developing a sampling plan based on C pk. Montgomery D (2009) Introduction to statistical quality control, 6th edn. Lin GH (2006) A hypothesis testing procedure on assessing process performance. Lepore A, Palumbo B, Castagliola P (2018) A note on decision making method for product acceptance based on process capability indices C pk and C pmk. Lepore A, Palumbo B (2015) New insights into the decisional use of process capability indices via hypothesis testing. Hussein A, Ahmed SE, Bhatti S (2012) Sequential testing of process capability indices. Hussein A (2005) Sequential comparison of two treatments using weighted wald-type statistics. Hubele NF, Vännman K (2004) The effect of pooled and un-pooled variance estimators on C pm when using subsamples. Kotz S, Lovelace CR (1998) Introduction to process capability indices: theory and practice. Kane VE (1986) Process capability indices. Int J Oper Res 3(1):56–75įeller W (1970) An Introduction to probability theory and its Applications, vol II. įan S, Kao C (2006) Development of confidence interval and hypothesis testing for Taguchi capability index using a Bayesian approach. Birkhäuser Verlag, BaselĬhen SM, Hsu YS (2004) Uniformly most powerful test for process capability index C pk. Springer, New Yorkīorodin AB, Salminen P (1996) Handbook of Brownian motion-facts and formulae. If \(T+C\) reaches \(N\), stop the test.Arizono I, Kanagawa A, Ohta H, Watakabe K, Tateishi K (1997) Variable sampling plans for normal distribution indexed by Taguchi’s loss function. If \(T-C\) reaches \(2\sqrt\), stop the test. Track the number of incoming successes from the control group. Track the number of incoming successes from the treatment group. The sequential procedure works like this:Īt the beginning of the experiment, choose a sample size \(N\).Īssign subjects randomly to the treatment and control, with 50% probability each.
#Sequential testing trial
Sequential sampling allows the experimenter to stop the trial early if the treatment appears to be a winner it therefore addresses the “peeking” problem associated with eager experimenters who use (abuse) traditional fixed-sample methods. In this post, I will describe a simple procedure for analyzing data in a continuous fashion via sequential sampling. Stopping an A/B test early because the results are statistically significant is usually a bad idea.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
